स्ट्रोक क्यों होता है? किन लोगों को ज्यादा खतरा है? कारण, लक्षण और इलाज
Why Does Stroke Happen? Who Is More at Risk? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
( Read in English language below )
( Apurba Das )
• स्ट्रोक क्या है?
स्ट्रोक (Stroke) तब होता है जब मस्तिष्क (Brain) को पर्याप्त रक्त और ऑक्सीजन नहीं मिल पाती। इसका कारण मस्तिष्क में रक्त प्रवाह का रुक जाना या रक्तस्राव (ब्लीडिंग) होना होता है। जब दिमाग की कोशिकाओं को कुछ मिनट तक ऑक्सीजन नहीं मिलती तो वे मरने लगती हैं, जिससे गंभीर शारीरिक विकलांगता या मौत तक हो सकती है। स्ट्रोक एक मेडिकल इमरजेंसी है और समय पर इलाज मिलना बेहद जरूरी होता है।
👉 स्ट्रोक के प्रकार
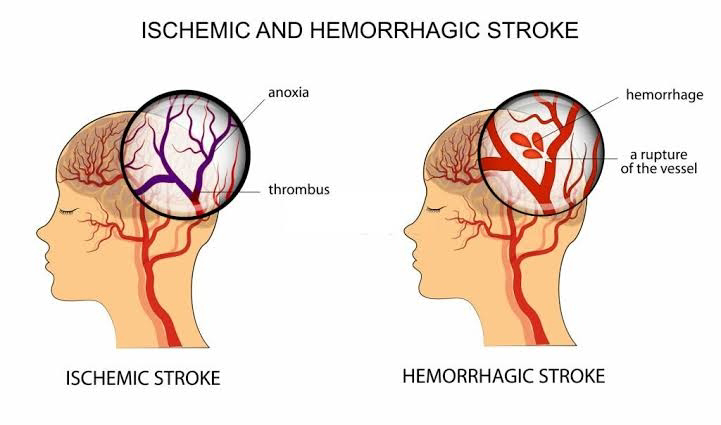
(1) इस्केमिक स्ट्रोक (Ischemic Stroke)
(2) सबसे ज्यादा सामान्य (करीब 87% मामलों में)
(2) मस्तिष्क की किसी रक्त धमनी में थक्का (Blood Clot) जम जाता है।
(3) खून का प्रवाह रुक जाता है।
(4) हेमरेजिक स्ट्रोक (Hemorrhagic Stroke)
(5) मस्तिष्क की रक्त नली फट जाती है।
(6) ब्लीडिंग होती है, जिससे दबाव बढ़ जाता है।
(7) टीआईए - ट्रांजिएंट इस्केमिक अटैक (Mini Stroke)
(8) अस्थायी रूप से रक्त प्रवाह रुकता है।
कुछ मिनटों या घंटों में सामान्य हो जाता है लेकिन यह भविष्य में बड़े स्ट्रोक का संकेत हो सकता है।
• स्ट्रोक के खतरे किन्हें ज्यादा हैं ?
(1) उम्र और लिंग: 55 वर्ष के बाद जोखिम तेजी से बढ़ता है।
पुरुषों में थोड़ा ज्यादा लेकिन महिलाओं में गंभीरता अधिक होती है।
👉 लेकिन याद रखिए आजकल कम उम्र में भी देखा गया है।
(2) आनुवांशिक कारण:
परिवार में स्ट्रोक का इतिहास होना।
(3) स्वास्थ्य संबंधी जोखिम:
• हाई ब्लड प्रेशर (Hypertension) – सबसे बड़ा कारण।
• डायबिटीज (Diabetes)
• कोलेस्ट्रॉल ज्यादा होना।
• दिल की बीमारियां।
• ओबेसिटी (मोटापा)
(4) जीवनशैली से जुड़े कारण:
• धूम्रपान
• शराब का अधिक सेवन
• शारीरिक गतिविधि की कमी
• गलत खानपान (फास्ट फूड, हाई फैट, ज्यादा नमक)
• ज्यादा मानसिक तनाव
(5) अन्य कारण:
• हार्मोनल गर्भनिरोधक गोलियां (Birth Control Pills)
• माइग्रेन (Migraine)
• कैंसर या अन्य गंभीर बीमारियां
👉 स्ट्रोक के मुख्य कारण (Reasons of Stroke)
(1) ब्लड प्रेशर बढ़ना:
लगातार हाई ब्लड प्रेशर से आर्टरी कमजोर हो जाती है और फट सकती है।
(2) ब्लड क्लॉट (थक्का) बनना:
आर्टरी में क्लॉट बनता है जो खून का बहाव रोक देता है।
(3) कोलेस्ट्रॉल का जमाव:
• आर्टरी में फैटी डिपॉजिट जमा हो जाते हैं।
• दिल की धड़कन अनियमित होना (Atrial Fibrillation):
• इससे खून का थक्का बनने का खतरा बढ़ता है।
(4) डायबिटीज:
• रक्त नलिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचाती है।
(5) धूम्रपान और शराब:
• खून की नलियों में सिकुड़न और ब्लॉकेज का कारण।
(6) तनाव और चिंता:
• ब्लड प्रेशर बढ़ाता है।
👉 स्ट्रोक के लक्षण (Symptoms of Stroke)
FAST फार्मूला:
• F (Face Drooping): चेहरे का एक भाग लटक जाना।
• A (Arm Weakness): एक हाथ में कमजोरी या उठाने में दिक्कत।
• S (Speech Difficulty): बोलने में अस्पष्टता, शब्दों का बिगड़ना।
• T (Time to Call Emergency): तुरंत डॉक्टर या एम्बुलेंस बुलाएं।
👉 अन्य लक्षण:
(1) अचानक तेज सिरदर्द।
(2) चक्कर आना या संतुलन बिगड़ना।
(3) एक आंख या दोनों में धुंधलापन या दिखना बंद होना।
(4) शरीर के एक हिस्से में सुन्नपन।
(5) भ्रम, याददाश्त में कमी।
(6) चलने-फिरने में दिक्कत।
👉 स्ट्रोक का निदान (Diagnosis)
(1) सीटी स्कैन (CT Scan) या एमआरआई (MRI) – स्ट्रोक का प्रकार और स्थान पता करने के लिए।
(2) ब्लड टेस्ट – शुगर, कोलेस्ट्रॉल, क्लॉटिंग लेवल जांचने के लिए।
(3) ईसीजी और ईकोकार्डियोग्राफी – दिल की स्थिति जानने के लिए।
(4) कारोटिड अल्ट्रासाउंड – गर्दन की धमनियों में ब्लॉकेज पता करने के लिए।
👉 स्ट्रोक का इलाज (Treatment)
(1) इस्केमिक स्ट्रोक में:
थ्रोम्बोलिटिक दवाएं (Clot-Busting Drugs):
जैसे tPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator) – स्ट्रोक के 4.5 घंटे के अंदर देने पर असरदार।
(2) मैकेनिकल थ्रोम्बेक्टॉमी: कैथेटर से थक्का हटाना।
(3) एंटीकोआगुलेंट और एंटीप्लेटलेट दवाएं:
खून पतला करने के लिए।
(4) हेमरेजिक स्ट्रोक में: ब्लीडिंग रोकने की दवाएं।
(5) जरूरत पड़ने पर सर्जरी – रक्तस्राव रोकना, स्कल डिकंप्रेशन।
• रिकवरी और रिहैबिलिटेशन:
(1) फिजियोथेरेपी
(2) स्पीच थेरेपी
(3) ऑक्यूपेशनल थेरेपी
(4) मनोवैज्ञानिक परामर्श
(5) स्ट्रोक से बचाव (Prevention)
• जीवनशैली में बदलाव:
(1) ब्लड प्रेशर कंट्रोल करें।
(2) डायबिटीज और कोलेस्ट्रॉल नियंत्रित करें।
(3) धूम्रपान और शराब बंद करें।
(4) नियमित व्यायाम करें – दिन में कम से कम 30 मिनट।
(5) संतुलित आहार लें – फल, सब्जी, कम नमक, कम फैट।
(6) तनाव कम करें – योग, ध्यान, मेडिटेशन।
(7) नियमित जांच:
साल में कम से कम एक बार ब्लड प्रेशर, शुगर, कोलेस्ट्रॉल की जांच कराएं।
👉 भारत में स्ट्रोक – खतरनाक आंकड़े
2022 में दुनियाभर में 1.22 करोड़ नए स्ट्रोक केस।
भारत में हर साल 18.5 लाख स्ट्रोक के मामले।
हर 4 मिनट में एक व्यक्ति स्ट्रोक से जान गंवा देता है।
25 साल से ज्यादा उम्र के हर 4 में से 1 व्यक्ति को जीवन में स्ट्रोक का खतरा।
स्ट्रोक एक जानलेवा लेकिन रोकथाम योग्य बीमारी है। समय पर लक्षण पहचानना, सही इलाज और जीवनशैली में सुधार से इस खतरे को काफी हद तक कम किया जा सकता है। याद रखें – “Time is Brain”, यानी स्ट्रोक में हर सेकंड कीमती है। जैसे ही लक्षण दिखें, तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें।
Why Does Stroke Happen? Who Is More at Risk? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
( Apurba Das )
What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the brain does not receive enough blood and oxygen. This happens either due to a blockage in blood flow or due to bleeding in the brain. When brain cells are deprived of oxygen for even a few minutes, they begin to die, leading to severe disability or even death. Stroke is a medical emergency, and timely treatment is critical to reduce damage.
👉 Types of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke:
Most common type (about 87% of all cases).
Occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain.
This blockage cuts off blood supply to brain tissues.
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Occurs when a blood vessel ruptures in the brain.
Causes bleeding, which increases pressure on the brain.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) – Mini Stroke:
A temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain.
Symptoms last a few minutes to hours and resolve on their own.
A warning sign of a possible major stroke in the future.
Who is at Higher Risk of Stroke?
1. Age and Gender:
• Risk increases significantly after age 55.
• Slightly more common in men, but women suffer more severe effects.
• Increasingly seen in younger people as well.
2. Genetic Factors:
Family history of stroke increases the risk.
3. Health Conditions:
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) – the biggest risk factor.
Diabetes.
High cholesterol.
Heart diseases.
Obesity (Overweight).
4. Lifestyle Factors:
Smoking.
Excessive alcohol consumption.
Lack of physical activity.
Unhealthy diet (high fat, high salt, junk food).
High mental stress.
5. Other Causes:
Hormonal birth control pills.
Migraine.
Cancer or other chronic diseases.
👉 Main Causes of Stroke
• High Blood Pressure:
Weakens arteries, which may burst.
• Blood Clots (Thrombosis):
Clots form inside arteries, blocking blood flow.
• Cholesterol Buildup (Atherosclerosis):
Fatty deposits narrow the arteries.
• Atrial Fibrillation (Irregular Heartbeat):
Increases the risk of blood clots.
• Diabetes:
Damages blood vessels over time.
• Smoking & Alcohol:
Causes artery narrowing and blockages.
• Stress & Anxiety:
Leads to elevated blood pressure.
• Symptoms of Stroke
Remember – FAST:
F – Face Drooping: One side of the face droops or feels numb.
A – Arm Weakness: Unable to lift one arm or weakness in one arm.
S – Speech Difficulty: Slurred or unclear speech.
T – Time to Call Emergency: Call a doctor or ambulance immediately.
👉Other Common Symptoms:
Sudden severe headache.
Dizziness or loss of balance.
Blurred vision in one or both eyes.
Numbness or weakness in one side of the body.
Confusion, memory problems.
Difficulty walking or loss of coordination.
👉 Diagnosis of Stroke
CT Scan or MRI:
Determines the type and location of the stroke.
Blood Tests:
Check sugar, cholesterol, and clotting factors.
ECG and Echocardiography:
Check for heart problems.
Carotid Ultrasound:
Detects blockages in neck arteries supplying the brain.
👉 Treatment of Stroke
For Ischemic Stroke:
Clot-Busting Medicines (Thrombolytics):
tPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator) is effective if given within 4.5 hours of stroke onset.
Mechanical Thrombectomy:
Removal of the blood clot using a catheter.
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs:
Blood thinners to prevent new clots.
👉 For Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Medicines to stop bleeding and reduce brain pressure.
Surgery if needed to stop bleeding or relieve
pressure on the brain (like skull decompression).
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Physiotherapy: Regain movement.
Speech Therapy: Improve speaking abilities.
Occupational Therapy: Manage daily activities independently.
Psychological Counseling: For emotional and mental health support.
👉 Stroke Prevention – How to Stay Safe:
Control Blood Pressure.
Manage Diabetes and Cholesterol.
Quit smoking and alcohol.
Exercise regularly – at least 30 minutes daily.
Eat a balanced diet – more fruits, vegetables, low salt, and low fat.
Reduce stress – through Yoga, Meditation, and Relaxation.
Get regular health check-ups – at least once a year (BP, Sugar, Cholesterol).
Stroke in India – Alarming Statistics
In 2022, there were 12.2 million new stroke cases worldwide.
In India, about 1.85 million people suffer from stroke every year.
One person dies every 4 minutes due to stroke in India.
1 in 4 people over the age of 25 are at risk of suffering a stroke in their lifetime.
Stroke is a life-threatening but preventable disease. Early detection, prompt treatment, and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk.
Always remember – “Time is Brain”, meaning every second counts during a stroke. If you notice any symptoms, seek immediate medical help.