सावधान! जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस आ रहा है: इसके लक्षण, कारण और बचाव के उपाय
Caution! Japanese Encephalitis is Spreading: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
( You can also read in English below 👇 )
( Apurba Das )
भारत सहित एशिया के कई देशों में बारिश के मौसम के दौरान मच्छरों से फैलने वाली बीमारियों का खतरा काफी बढ़ जाता है। इन्हीं खतरनाक बीमारियों में से एक है जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस (Japanese Encephalitis)। यह बीमारी मस्तिष्क (Brain) को प्रभावित करती है और कई बार जानलेवा भी साबित होती है। आइए जानते हैं जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस क्या है, इसके लक्षण, कारण और बचाव के उपाय।
जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस क्या है?
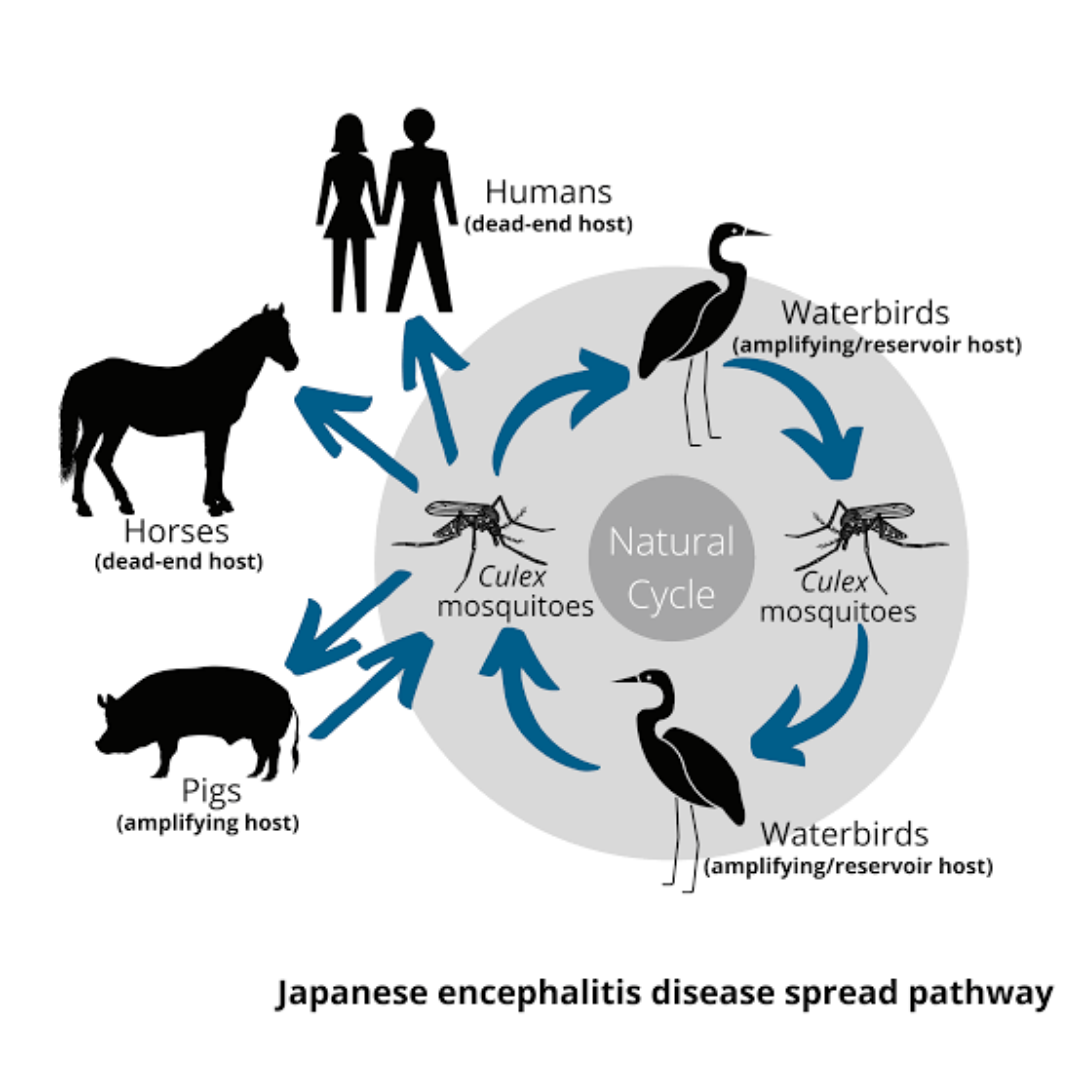
जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस (JE) एक वायरल बीमारी है, जो मच्छरों के काटने से फैलती है। यह बीमारी मुख्य रूप से मस्तिष्क में सूजन (Encephalitis) पैदा करती है। इस बीमारी का वायरस 'फ्लेविवायरस (Flavivirus)' नामक श्रेणी का होता है। यह वायरस संक्रमित सूअर (Pig) और जंगली पक्षियों से मच्छरों के माध्यम से इंसानों में फैलता है।
इस बीमारी का सबसे ज्यादा असर छोटे बच्चों और बुजुर्गों पर होता है क्योंकि उनकी रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता कमजोर होती है।
• जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस के लक्षण :
इस बीमारी के लक्षण मच्छर के काटने के कुछ दिनों बाद दिखाई देते हैं। कई मामलों में शुरुआत में लक्षण बहुत हल्के होते हैं, लेकिन धीरे-धीरे गंभीर हो जाते हैं।
मुख्य लक्षण निम्न हैं:
तेज बुखार (High Fever)
सिरदर्द (Severe Headache)
मांसपेशियों में दर्द (Muscle Pain)
थकान और कमजोरी (Fatigue and Weakness)
उल्टी या मतली (Nausea and Vomiting)
बेहोशी या मानसिक भ्रम (Unconsciousness or Mental Confusion)
दौरे पड़ना (Seizures)
गर्दन में अकड़न (Neck Stiffness)
चलने-फिरने में असमर्थता (Difficulty in Movement)
बेहोशी या कोमा (Coma in severe cases)
अगर समय पर इलाज न हो, तो यह रोग मस्तिष्क को इतना नुकसान पहुंचा सकता है कि मरीज का जीवन खतरे में पड़ सकता है या स्थायी विकलांगता हो सकती है।
• जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस के कारण :
यह बीमारी मुख्यतः निम्न कारणों से फैलती है:
मच्छरों के काटने से:
खासकर Culex प्रजाति के मच्छर जो संक्रमित होते हैं।
संक्रमित सूअर और पक्षी:
मच्छर पहले संक्रमित सूअर या जंगली पक्षियों का खून चूसते हैं और फिर इंसानों को काटते हैं।
गंदगी और पानी का जमाव:
बारिश के मौसम में जहां पानी जमा होता है, वहां मच्छरों का प्रजनन तेजी से होता है।
खेती-किसानी के इलाकों में ज्यादा खतरा:
धान के खेतों में पानी भरा रहता है, जो मच्छरों के प्रजनन का प्रमुख केंद्र होता है।
ग्रामीण इलाकों में ज्यादा फैलाव:
जहां स्वास्थ्य सुविधाएं सीमित होती हैं और लोग जागरूक नहीं होते।
• बीमारी किन लोगों को ज्यादा प्रभावित करती है?
छोटे बच्चे (1 से 15 साल तक)
बुजुर्ग व्यक्ति
कमजोर इम्यून सिस्टम वाले लोग
किसान, पशुपालक और ग्रामीण क्षेत्र के निवासी
• जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस से बचाव के उपाय
1. मच्छरों से बचाव करें:
अपने घर और आस-पास पानी जमा न होने दें।
सोते समय मच्छरदानी का प्रयोग करें।
मच्छर भगाने वाली क्रीम (Repellent) लगाएं।
खिड़की और दरवाजों पर जाली लगवाएं।
2. स्वच्छता बनाए रखें:
आसपास के नालों और गड्ढों में पानी न जमा होने दें।
कचरा और गंदगी समय पर साफ करें।
जल निकासी की उचित व्यवस्था करें।
3. टीकाकरण (Vaccination):
जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस से बचाव के लिए टीका उपलब्ध है।
भारत सरकार कई राज्यों में JE का फ्री टीकाकरण अभियान चलाती है।
बच्चों को यह टीका अनिवार्य रूप से लगवाएं।
4. व्यक्तिगत सावधानी:
बच्चों और बुजुर्गों को शाम के समय बाहर जाने से बचाएं।
फुल बांह के कपड़े पहनें।
धान के खेतों या जलभराव वाली जगहों पर विशेष सावधानी बरतें।
5. समय पर इलाज:
अगर बुखार, सिरदर्द या दौरे जैसे लक्षण दिखें तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें।
समय पर इलाज से जान बचाई जा सकती है।
जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस का इलाज :
इस बीमारी का कोई विशेष एंटीवायरल इलाज नहीं है। इलाज मुख्यतः लक्षणों को कम करने और मरीज की स्थिति को संभालने पर आधारित होता है।
• इलाज में शामिल हैं:
तेज बुखार और सिरदर्द को नियंत्रित करना।
दवाइयों से दौरे (Seizures) को रोकना।
मरीज को तरल पदार्थ और पोषण देना।
गंभीर मामलों में ICU में भर्ती कराना।
सांस लेने में तकलीफ हो तो ऑक्सीजन देना।
समय पर इलाज न हो तो मृत्यु दर बहुत अधिक हो जाती है।
• किन राज्यों में ज्यादा खतरा?
भारत में जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस सबसे ज्यादा निम्न राज्यों में देखा जाता है:
उत्तर प्रदेश
बिहार
असम
पश्चिम बंगाल
झारखंड
मणिपुर
नगालैंड
ओडिशा
इन राज्यों के ग्रामीण इलाकों में बारिश के मौसम में इसका प्रकोप ज्यादा होता है।
• सरकार द्वारा उठाए गए कदम :
मुफ्त टीकाकरण अभियान।
मच्छर रोधी दवाओं का छिड़काव।
ग्रामीण स्वास्थ्य शिविरों का आयोजन।
जन जागरूकता अभियान।
जापानी इंसेफेलाइटिस एक खतरनाक बीमारी है, लेकिन इससे बचाव संभव है। यदि लोग जागरूक रहें, साफ-सफाई का ध्यान रखें, मच्छरों से बचाव करें और बच्चों का टीकाकरण समय पर कराएं, तो इस बीमारी से खुद को और अपने परिवार को सुरक्षित रखा जा सकता है।
सावधान रहें, सुरक्षित रहें, और अपने स्वास्थ्य का ध्यान रखें।
Caution! Japanese Encephalitis is Spreading: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
( Apurba Das )
During the rainy season, mosquito-borne diseases increase rapidly in many Asian countries, including India. One such dangerous and potentially fatal disease is Japanese Encephalitis (JE). This disease mainly affects the brain and can lead to serious complications if not treated in time. In this article, we will discuss what Japanese Encephalitis is, its symptoms, causes, and effective prevention measures.
What is Japanese Encephalitis?
Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. It causes inflammation in the brain (encephalitis) and can become life-threatening. The disease is caused by the Flavivirus, which belongs to the same group of viruses responsible for dengue, yellow fever, and West Nile virus.
The virus spreads mainly through the bite of infected mosquitoes that have previously fed on infected pigs or wild birds. Japanese Encephalitis primarily affects children, the elderly, and people with weak immune systems.
Symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis
The symptoms generally appear within 5 to 15 days after the bite of an infected mosquito. In some cases, the initial symptoms are mild but can worsen rapidly.
Common Symptoms Include:
High fever
Severe headache
Muscle pain and stiffness
Fatigue and extreme weakness
Nausea and vomiting
Confusion, disorientation, or unconsciousness
Seizures (fits)
Neck stiffness
Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
Coma in severe cases
If left untreated, this disease can cause permanent brain damage, paralysis, or even death.
Causes of Japanese Encephalitis
How does it spread?
The disease is primarily spread through the bite of infected Culex mosquitoes.
These mosquitoes become infected by feeding on infected pigs or wild birds.
The virus does not spread directly from person to person.
• Major Causes Include:
Stagnant water: Mosquitoes breed in areas where water accumulates, like rice fields, ponds, and open drains.
Proximity to livestock: People living near pig farms are at higher risk.
Rural areas: The disease is more prevalent in villages where sanitation is poor and water logging is common.
Monsoon season: The risk increases during the rainy season due to higher mosquito breeding.
• Who is at higher risk?
Children aged 1–15 years
Elderly individuals
People with weak immune systems
Farmers, livestock handlers, and people living in rural or flood-prone areas
• Prevention of Japanese Encephalitis
1. Protection from Mosquitoes:
Keep your surroundings clean and dry. Avoid water stagnation.
Use mosquito nets while sleeping.
Apply mosquito repellents on exposed skin.
Install mesh screens on windows and doors to keep mosquitoes out.
Wear long-sleeved clothes especially during evening and night.
2. Maintain Cleanliness:
Regularly clean drains, water tanks, and other places where water can accumulate.
Dispose of garbage properly.
Fill pits, potholes, and unused containers that may collect water.
3. Vaccination:
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent JE.
The Japanese Encephalitis vaccine is available and is often provided free in many states of India under government health programs.
Ensure children receive the JE vaccine, especially in high-risk areas.
4. Personal Precautions:
Avoid outdoor activities during dusk and dawn when mosquitoes are most active.
Be cautious while visiting or working in agricultural fields, particularly rice paddies.
5. Seek Medical Help Promptly:
If anyone experiences high fever, headache, confusion, or seizures, consult a doctor immediately.
Early diagnosis and treatment can save lives.
Treatment of Japanese Encephalitis
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Japanese Encephalitis. The management is mainly supportive, aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
Treatment includes:
Controlling fever and headaches with medicines.
Managing seizures with appropriate medications.
Providing adequate fluids and nutrition.
Oxygen support if breathing difficulty occurs.
Intensive care in severe cases (ICU support).
Delay in treatment can lead to severe brain damage, coma, or death.
States in India Most Affected by JE:
Uttar Pradesh
Bihar
Assam
West Bengal
Jharkhand
Manipur
Nagaland
Odisha
These states report frequent outbreaks, especially in rural and low-lying areas during the monsoon season.
• Government Initiatives to Fight JE:
Free vaccination drives in high-risk areas.
Spraying insecticides in mosquito breeding zones.
Health camps in rural areas for early diagnosis and treatment.
Public awareness campaigns to educate people about prevention.
Key Facts about Japanese Encephalitis:
JE is not contagious from person to person.
The majority of infections are asymptomatic (show no symptoms).
About 1 in 250 infections develop into severe encephalitis.
The mortality rate in severe cases is 20–30%.
Survivors can suffer from long-term neurological complications like paralysis, speech difficulties, and memory problems.
Japanese Encephalitis is a serious but preventable disease. The key to protection lies in mosquito control, maintaining cleanliness, timely vaccination, and early medical intervention. Public awareness and personal precautions can significantly reduce the risk of this dangerous infection.
Let’s stay safe, stay healthy, and protect ourselves and our families from Japanese Encephalitis.